In the future, the next-generation Mars exploration project will install an instrument that can survey Martian atmosphere maps around the clock and can detect possible gas evidence of Mars life.
The new detector, called the "Mars climate detector," measures the vertical distribution of air, dust, water vapor, and ice crystals between the two poles of Mars' atmosphere. The instrument is one of the five instruments assembled by the European-United States aviation survey mission, the external Mars tracking gas orbiter, and is scheduled to be launched in 2016. It will also search for gas evidence of potential life on Mars.
The atmosphere map taken by the Mars climate detector will provide daily changes in the Martian atmosphere. In addition to performing gas tracking detection, the instrument will also complete two important tasks. One is to expand the current NASA MARS Orbiter's mapping record of Mars climate; the other is to provide information on Mars atmosphere density changes, which will help to assess the future Mars landing site. NASA’s chief investigator for the Mars Climate Probe at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Tim Schofield, said: “We expect the instrument to provide climate background information on selected landing sites, relevant seasonal characteristics, and different time periods of the day. It also provides near-real-time information on the atmospheric structure of the Mars spacecraft landing site after the successful launch in 2016."
The Mars Climate Detector is an infrared radiometer that can continuously observe the surface of Mars from an altitude of 400 kilometers. The focus of the external Mars tracking gas orbiter is to collect methane gas that can confirm the potential biological activity of Mars.
The new detector, called the "Mars climate detector," measures the vertical distribution of air, dust, water vapor, and ice crystals between the two poles of Mars' atmosphere. The instrument is one of the five instruments assembled by the European-United States aviation survey mission, the external Mars tracking gas orbiter, and is scheduled to be launched in 2016. It will also search for gas evidence of potential life on Mars.
The atmosphere map taken by the Mars climate detector will provide daily changes in the Martian atmosphere. In addition to performing gas tracking detection, the instrument will also complete two important tasks. One is to expand the current NASA MARS Orbiter's mapping record of Mars climate; the other is to provide information on Mars atmosphere density changes, which will help to assess the future Mars landing site. NASA’s chief investigator for the Mars Climate Probe at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Tim Schofield, said: “We expect the instrument to provide climate background information on selected landing sites, relevant seasonal characteristics, and different time periods of the day. It also provides near-real-time information on the atmospheric structure of the Mars spacecraft landing site after the successful launch in 2016."
The Mars Climate Detector is an infrared radiometer that can continuously observe the surface of Mars from an altitude of 400 kilometers. The focus of the external Mars tracking gas orbiter is to collect methane gas that can confirm the potential biological activity of Mars.
Paper Making Pulping And Approach System
This is Paper Making Machine pulping and approaching system, which is working together with paper making machine. It can use raw materials such as wood dust, rice straw, wheat straw, reed straw, cotton stalk etc, from which can make virgin pulp to for the paper making machine to produce different kinds of paper.
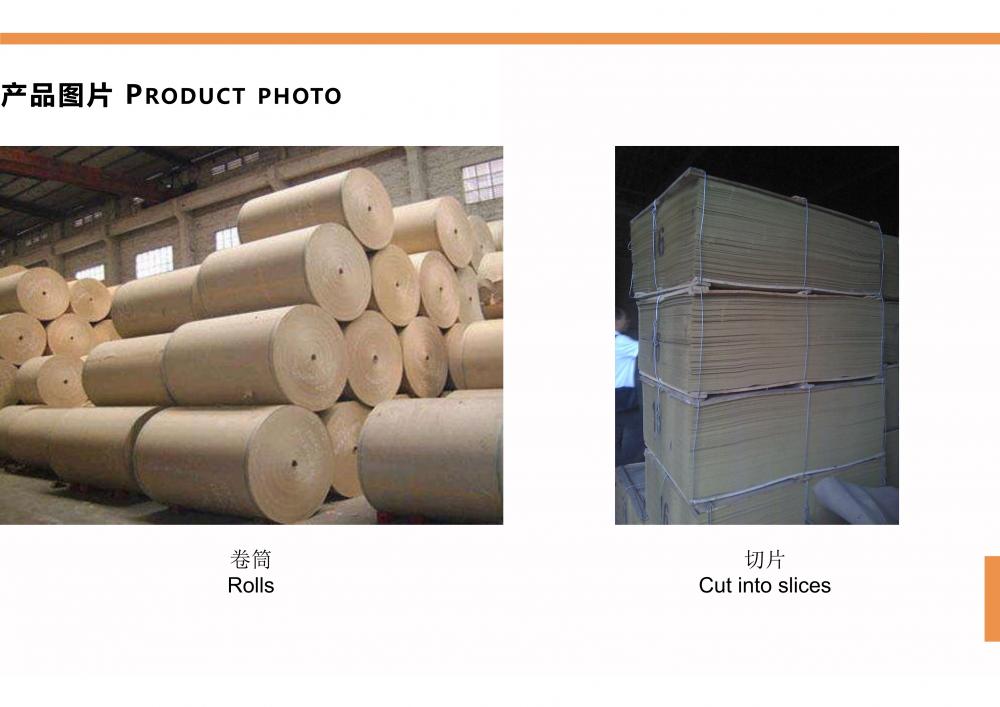
Paper Pulp Machine,Straw Pulp Making Machinery,Cotton Pulp Making Machine,Paper Making Pulping And Approach System
Dandong Tianshin Automatization Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.tianshinmachine.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)